
A high ankle sprain happens when the ligaments that hold the two lower leg bones together, just above the ankle, are stretched or torn. This usually occurs when the foot twists outward or is pushed upward with force, as may be common during sports activities. Symptoms of a high ankle sprain include pain while walking, especially when trying to rise onto the toes, but there may not be much swelling at first. Because this type of sprain affects deeper parts with the ankle joint, it can be harder to diagnose without proper testing. A podiatrist can examine the ankle and may order X-rays or more detailed scans to look for signs of torn ligaments or broken bones. If the bones have moved apart, surgery may be needed to hold them in place while the area heals. If the bones are still aligned, a cast or walking boot may be used to keep weight off the ankle while it recovers. If you have sprained an ankle, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for an exam, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment.
Although ankle sprains are common, they aren’t always minor injuries. If you need your ankle injury looked at, contact Dr. Paul Drucker from NYC Foot Care, PC. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
How Does an Ankle Sprain Occur?
Ankle sprains are the result of a tear in the ligaments within the ankle. These injuries may happen when you make a rapid shifting movement while your foot is planted. A less common way to sprain your ankle is when your ankle rolls inward while your foot turns outward.
What Are the Symptoms?
- Pain at the sight of the tear
- Bruising/Swelling
- Ankle area is tender to touch
- In severe cases, may hear/feel something tear
- Skin discoloration
Preventing a Sprain
- Wearing appropriate shoes for the occasion
- Stretching before exercises and sports
- Knowing your limits
Treatment of a Sprain
In many cases, the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevate) is used to treat ankle sprains. However, you should see a podiatrist to see which treatment option would work best with your injury. In severe cases, surgery may be required.
It is important to ask your doctor about rehab options after you receive treatment for your injury. Stretching, strength training, and balance exercises may help the ankle heal while also preventing further injury.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in 70th Street Manhattan, 60th Street Manhattan, Jamaica, Queens, Plainview, NY and Fair Lawn, NJ . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.

Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that results from the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It often causes sudden and severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness, and most commonly affects the big toe. The pain may start at night and can be intense enough to wake someone from sleep. Gout is accompanied by severe pain, causing difficulty in completing daily activities. Several factors increase the risk of developing gout. These include a diet high in red meat or seafood, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and certain health conditions such as hypertension or kidney disease. Genetics may also play a role. If you have pain in the joints of your feet, particularly the big toe, it is strongly suggested that you are under the care of a podiatrist who can diagnose gout and offer management options.
Gout is a foot condition that requires certain treatment and care. If you are seeking treatment, contact Dr. Paul Drucker from NYC Foot Care, PC. Our doctor will treat your foot and ankle needs.
What Is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream. It often develops in the foot, especially the big toe area, although it can manifest in other parts of the body as well. Gout can make walking and standing very painful and is especially common in diabetics and the obese.
People typically get gout because of a poor diet. Genetic predisposition is also a factor. The children of parents who have had gout frequently have a chance of developing it themselves.
Gout can easily be identified by redness and inflammation of the big toe and the surrounding areas of the foot. Other symptoms include extreme fatigue, joint pain, and running high fevers. Sometimes corticosteroid drugs can be prescribed to treat gout, but the best way to combat this disease is to get more exercise and eat a better diet.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our offices located in 70th Street Manhattan, 60th Street Manhattan, Jamaica, Queens, Plainview, NY and Fair Lawn, NJ . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
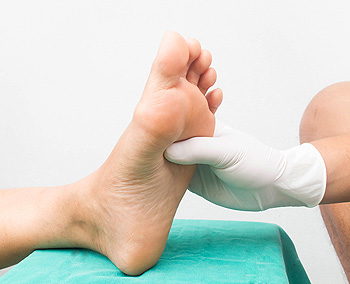
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition involving damage to the peripheral nerves, often affecting the feet, toes, and ankles. Patients may experience numbness, tingling, burning sensations, or sharp, stabbing pain that tends to worsen at night. As the sensory nerves in the feet become damaged, there is a reduced ability to feel temperature changes or pain, which can increase the risk of unnoticed injuries, infections, and foot ulcers. Over time, this nerve damage can also weaken the muscles in the feet and ankles, resulting in instability and difficulty walking. Diabetes is a common cause of peripheral neuropathy, and long-term high blood sugar levels can further harm nerves and the small blood vessels that supply them. Other contributing factors include alcohol misuse, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medical conditions. A podiatrist can help manage symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and monitor nerve health through regular foot exams. In more advanced cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on specific nerves. If you have symptoms of peripheral neuropathy affecting your feet, it is suggested that you schedule an appointment with a podiatrist for an exam and ongoing treatment.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy can be a potentially serious condition, especially if it is left undiagnosed. If you have any concerns that you may be experiencing nerve loss in your feet, consult with Dr. Paul Drucker from NYC Foot Care, PC. Our doctor will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment for neuropathy.
What Is Neuropathy?
Neuropathy is a condition that leads to damage to the nerves in the body. Peripheral neuropathy, or neuropathy that affects your peripheral nervous system, usually occurs in the feet. Neuropathy can be triggered by a number of different causes. Such causes include diabetes, infections, cancers, disorders, and toxic substances.
Symptoms of Neuropathy Include:
- Numbness
- Sensation loss
- Prickling and tingling sensations
- Throbbing, freezing, burning pains
- Muscle weakness
Those with diabetes are at serious risk due to being unable to feel an ulcer on their feet. Diabetics usually also suffer from poor blood circulation. This can lead to the wound not healing, infections occurring, and the limb may have to be amputated.
Treatment
To treat neuropathy in the foot, podiatrists will first diagnose the cause of the neuropathy. Figuring out the underlying cause of the neuropathy will allow the podiatrist to prescribe the best treatment, whether it be caused by diabetes, toxic substance exposure, infection, etc. If the nerve has not died, then it’s possible that sensation may be able to return to the foot.
Pain medication may be issued for pain. Electrical nerve stimulation can be used to stimulate nerves. If the neuropathy is caused from pressure on the nerves, then surgery may be necessary.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in 70th Street Manhattan, 60th Street Manhattan, Jamaica, Queens, Plainview, NY and Fair Lawn, NJ . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.

